Knowledge
Fiber Optic Cable Duct Pulling Techniques 2025
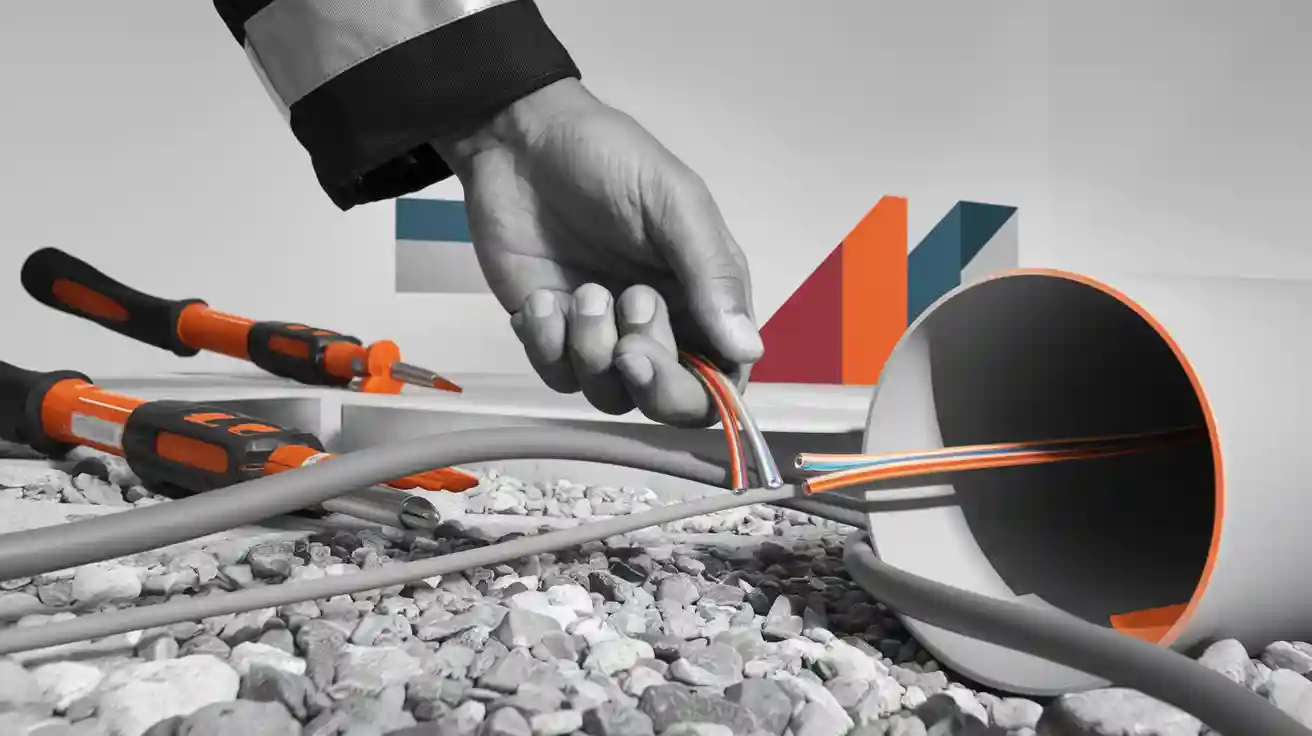

You are very important in making fiber optic cable last long by using the right cable duct pulling methods. More than half of cable problems happen because of wrong pulling. In 2025, new tools like hydraulic blowers, smart monitors, and better grips help you lower risks, save money, and keep the network working well.
Key Takeaways
-
Use the correct pulling ways and tools. This helps keep fiber optic cables safe from harm and signal problems when you put them in. Plan your path well. Use the right lubricant. Follow the rules for tension and bend radius. This makes sure the cable pull is smooth and safe. Try new methods like air blowing. Use smart monitoring devices. These help you work faster, lower risks, and make the installation better.
Cable Duct Pulling Basics
Mastering duct pulling fundamentals requires precise tension control, specialized lubricant application, and optimal equipment selection to minimize friction and prevent cable damage during installation—core skills for efficient fiber deployment.
Fiber Optic Cable Protection
You help keep fiber optic cable safe when you install it. Cable duct pulling means moving the cable through a duct with pull tape. You use tools like pulleys and pulling eyes to protect the cable. Always look at the cable’s strength members, like aramid yarn, before starting. These parts take the pulling force and stop the fibers from breaking. If you pull on the jacket, not the strength member, you can hurt the cable. This can make the signal worse. You should use good methods to keep the cable safe for long distances.
Duct Fiber Optic Cable Methods
You can pick manual or mechanical pulling for duct fiber optic cable. Manual pulling is good for short runs. Mechanical pulling uses machines for longer pulls. Before pulling, clean the duct and check for anything blocking it. Lubrication makes pulling easier and safer by lowering friction. Plan the path and use the right grips to stop twisting or crushing the cable.
Tip: Always check the highest pulling tension and smallest bend radius before you start.
Tension and Bend Radius
You must know the pulling tension and bend radius limits. Most fiber optic cable can take up to 600 pounds-force (2670 N). Premises cables can only take 50 pounds (222 N). The smallest bend radius during installation is usually 20 times the cable’s width. After you finish, you can use a bend radius of 10 times the width.
|
Cable Type |
Max Pulling Tension |
Min Bend Radius (Install) |
Min Bend Radius (Static) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Premises Cable |
50 lbs (222 N) |
50 mm |
25 mm |
|
Outside Plant Cable |
600 lbs (2670 N) |
20x cable diameter |
10x cable diameter |
To keep the cable safe, use this formula:Pulling Tension = Cable Weight x Length x Coefficient of Friction (COF)
Less friction means you can pull farther without hurting the cable.
Installation of Duct Fibre Optic Cable Techniques
Integrating nanoparticle lubricants, real-time tension monitoring, and intelligent pulling systems forms the core of 2025 duct installation, preventing cable jacket damage while optimizing deployment speed across varied conduit environments.

Manual and Mechanical Pulling
You can use manual or mechanical pulling when you install fiber optic cable into ducts. Manual pulling means you and your team pull the cable by hand. Mechanical pulling uses a machine to help you pull the cable through the duct. Both methods work best for short to medium distances.
Here is a table to help you see the differences:
|
Aspect |
Manual Pulling |
Mechanical Pulling (Machine-Assisted) |
|---|---|---|
|
Efficiency (Pull Rate) |
Slow, needs more time |
Faster (~50 feet per minute) |
|
Labor Requirements |
High, needs many workers |
Needs fewer workers, but still some labor |
|
Assist Points |
Many, for twists and turns |
Needed, but less frequent |
|
Risk of Cable Damage |
Higher, more friction and twisting |
Lower, but still possible |
|
Equipment Movement |
Frequent, slows down the process |
Less frequent, more streamlined |
Manual pulling takes more effort and time. You must watch for friction and twisting, which can damage the cable. Mechanical pulling helps you move faster and reduces some risks, but you still need to check the cable often. Always use pulling eyes and grips to protect the cable’s strength members. Never pull on the cable jacket alone.
Tip: Use a break-away swivel to stop the cable from twisting and to keep the pulling force safe.
Air Blowing Method
Air blowing is a modern way to install fiber optic cable. You use a machine that pushes the cable with high-speed air through the duct. This method works best for long distances, even up to 5.3 kilometers in one go, as shown in recent case studies.
Why choose air blowing?
-
You finish the installation faster.
-
You need fewer workers and less heavy equipment.
-
You lower the risk of cable damage because there is less tension and friction.
-
You can install cable over long distances, even with bends and hills.
-
You save money on labor and materials because you need fewer splice points and handholes.
Air blowing is now the top choice for long runs and complex routes. You can use it in places where pulling would be too slow or risky.
Note: Air blowing works best when you prepare the duct well and use the right equipment.
Equipment and Preparation
You need the right tools and a good plan for a safe and smooth installation of duct fibre optic cable. Here is a checklist to help you get ready:
-
Essential Tools:
-
Fiber optic cleavers and strippers
-
Pulling eyes and grips
-
Cable rollers and duct rodder tools
-
Lubricants for reducing friction
-
Cable ties and clamps
-
Fiber blowing machine (for air blowing)
-
Testing equipment: OTDR, light source, power meter
-
-
Preparation Steps:
-
Inspect the duct for debris, water, or damage.
-
Test the duct to make sure it is clear and dry.
-
Check the cable specifications for maximum tension and bend radius.
-
Plan your route. Map out pulling points, assist points, and cable feed locations.
-
Make sure the environment is safe and meets all requirements.
-
Set up all equipment and test it before starting.
-
Route planning is very important. When you plan the route, you avoid problems like sharp bends, obstacles, or places where the cable could get stuck. Good planning helps you use your time and resources better. It also keeps the cable safe and helps you follow all rules and standards.
Tip: Always use the right amount of lubricant. For every 30 meters of duct, use at least 500 ml. This lowers the pulling force by about 35%.
Safety and Best Practices
You must follow safety rules to protect yourself and the fiber optic cable during installation. Here are the most important steps:
-
Keep only skilled workers near the pulling area during tensioning.
-
Use warning signs to keep others away from the work zone.
-
Wear leather gloves when handling cable and rubber gloves near electrical circuits.
-
Never bend the cable tighter than its minimum bend radius.
-
Use grips with swivels and the right lubricant to reduce tension and twisting.
-
Inspect all poles and ducts for hazards before you start.
-
Control the cable pay-off to stop tangling.
-
Use auto shut-off tuggers and large sheave wheels to keep tension and bend radius safe.
-
After installation, check slack coils to make sure the bend radius is correct.
-
Test the fiber for damage before you finish the job.
-
Store cable reels on solid ground and keep ducts dry.
You should always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines. These rules help you avoid damage, signal loss, and costly repairs. The guidelines tell you the right bend radius, pulling tension, and temperature range for installation. They also remind you to use personal protective equipment like safety glasses and boots.
Alert: Training is key. Make sure everyone on your team knows how to handle fiber optic cable, follow safety codes, and use the right tools.
After you finish the installation, protect the cable and duct system:
-
Test the fiber optic duct to make sure it is free from defects.
-
Inspect the cable and duct regularly for water or physical damage.
-
Fix any problems right away to keep the network running well.
-
Use strong materials like HDPE ducts for extra protection.
-
Keep the duct system in good shape to make your network last longer.
By following these steps, you make sure your fiber optic cable installation is safe, reliable, and ready for the future.
Advanced Solutions and Risk Management
Deploying AI tension controllers, blockchain-lubricant tracking, and predictive strain analytics mitigates installation risks—transforming duct pulls into data-driven operations that prevent costly cable breaks and compliance violations.
Smart Monitoring Devices
You can use smart monitoring devices to make cable installation safer. These devices help you install fiber optic cable more accurately. AI-assisted pulling systems have sensors and controls. They find alignment problems and fix the cable right away. GPS tracking and laser guidance show you where to put the cable. This helps you make fewer mistakes and do less rework. These systems work with many cable types and sizes. You can change the settings for each job. Automated pulling saves money on workers and finishes projects faster. In one job, an anti-rotation device stopped the cable from twisting. It also kept the fiber strands safe. You get better results when you use smart tools, good training, and safety checks together.
Friction Issues and Lubrication
Friction is a big problem when you pull cable. Too much friction can hurt the cable jacket and make it work worse. Friction happens a lot when the duct has many bends or bumps. The tension can go up fast and make pulling unsafe. You should use cable-pulling lubricants to lower friction and tension. Water-based lubricants like Techlube FO stick to the cable and duct walls. They work even when things are wet. Cable blowing lubricants spread out and stop cables from sticking together. Always put lubricant on the cable and duct evenly. This helps you stop cable damage and makes the job easier.
Compliance and Cost Control
You need to manage risks and follow rules to control costs. Stopping cable damage saves money on repairs and keeps the network working. Training your team and keeping good records help you avoid mistakes. This also stops service from being interrupted. Labor is the biggest cost, so plan your work and use your crew well. Do surveys before you start to find problems early. Get permits before you begin. Buy materials in bulk to save money. Plan for the future by putting in extra conduit now. This can save money later. Follow standards like EN 50411-2-6 to keep tension and temperature safe.
You get the best results when you use good pulling techniques for fiber optic cable installation.
|
Technique |
Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Automated Pullers |
Less mistakes, safer work |
|
Lubricants |
Less rubbing, easier job |
|
Proper Routing |
Stops cable from getting hurt |
-
Always check how tight the cable is and how much it bends.
-
Use the right tools and wear safety equipment.
-
Keep your test results neat so you can fix problems fast.

 Fiber Optic Termination Boxes
Fiber Optic Termination Boxes Fiber Optic Splice Enclosures
Fiber Optic Splice Enclosures Fiber Patch Panels
Fiber Patch Panels PLC Splitters
PLC Splitters Fiber Optic Pigtails
Fiber Optic Pigtails OTDR Launch Cables
OTDR Launch Cables Fiber Optic Adapters
Fiber Optic Adapters Fiber Optic Patch Cords
Fiber Optic Patch Cords