Knowledge
Building the Foundation: Ensuring Success in Fiber Termination Box Installation

Understanding Fiber Termination Boxes
Fiber termination boxes are indispensable components in modern fiber optic communication systems. They are designed to manage and protect the delicate optical fibers that transmit data over vast distances. As we delve into the world of fiber optics, understanding the role and variety of fiber termination boxes is fundamental for those involved in their installation and maintenance.
Importance of Fiber Termination Boxes
A fiber termination box acts as a crucial intermediary between the fiber optic cable and the pigtail, connecting them through splicing. These boxes serve multiple functions, including routing, distribution, and protection of fiber optic cables (FiberCheap). By housing and organizing the splices where cables are terminated, these boxes ensure that the fiber connection points are well-protected against environmental factors and potential damage.
In Fiber to the Home (FTTH) networks, for example, termination boxes are used to distribute optical fiber links and safeguard them from external impact. They enable a seamless transition from outdoor to indoor wiring and provide a central point for the network’s optical cables to be managed and maintained (STL.tech).
Types of Fiber Termination Boxes
Fiber termination boxes come in various forms, each tailored to specific needs based on the number of fibers fused, the cable connection method, and the material of the shell. Here are some common types of fiber termination boxes:
- Rack-drawer Type: Ideal for server rooms and data centers, these boxes provide high-density fiber distribution and can be easily integrated into a rack system.
- Wall-mounted Type: Suited for both indoor and outdoor applications, these boxes are designed to save space and are commonly found in residential and commercial settings. For more details on wall-mounted options, visit our fiber termination box wall-mount page.
- Desktop Type: Perfect for smaller-scale applications or where a dedicated wall space is not available, these boxes are compact and can be placed on a desk or shelf.
The selection of a fiber termination box often depends on the specific requirements of the network and the environment in which it will be installed. The box must accommodate the right number of fibers and offer the necessary protection to ensure the longevity and reliability of the fiber optic network.
| Fiber Termination Box Type | Common Use Case |
|---|---|
| Rack-drawer | Server rooms, Data centers |
| Wall-mounted | Indoor/outdoor residential and commercial buildings |
| Desktop | Small-scale applications, temporary setups |
The type of fiber termination box also influences the cost, and those interested in pricing information can check the fiber termination box price page for a comprehensive guide.
By recognizing the significance of fiber termination boxes and the various types available, we can better appreciate their role in the broader fiber optic network. They not only facilitate the organization and protection of the optical fibers but also contribute to the overall efficiency and success of the communication system.
Installation of Fiber Termination Boxes
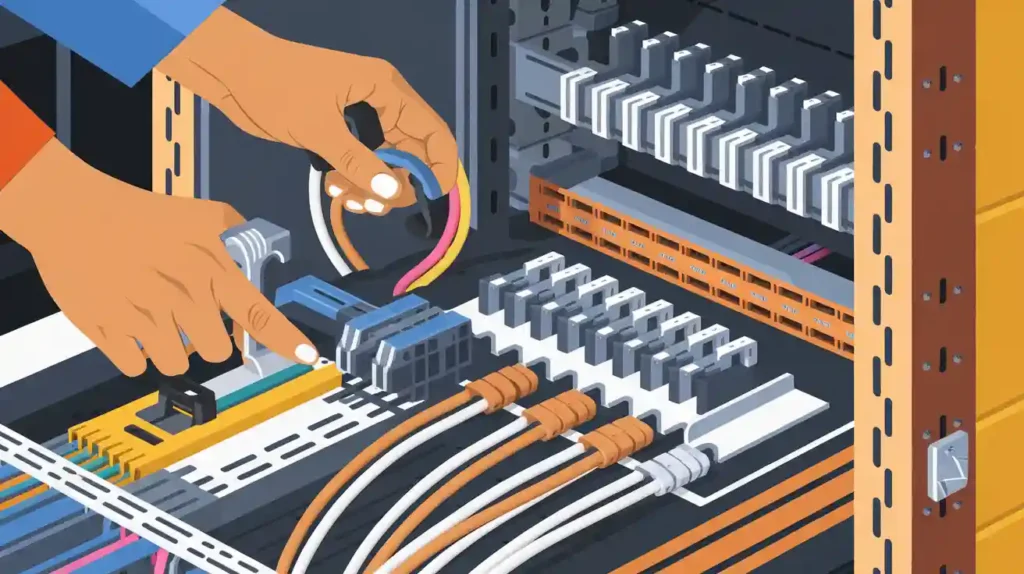
Proper installation of fiber termination boxes is critical for ensuring the efficiency and reliability of a fiber optic network. Here, we’ll walk through the necessary steps and tools to ensure that your fiber termination box installation meets industry standards and provides optimal performance for your network’s needs.
Steps for Installing Fiber Termination Boxes
- Preparation: Begin by assessing the installation site to ensure it is suitable for the fiber termination box. Consider factors such as ease of access, protection from environmental elements, and proximity to the equipment you’ll be connecting to.
- Mounting the Box: Depending on the type of fiber termination box, mount it either on the wall or a standard rack. For wall mounting solutions, visit our fiber termination box wall mount page for more details.
- Preparing the Cable Ends: Strip the fiber optic cables to the appropriate length, ensuring you remove the outer jacket, buffer, and cladding without damaging the fiber.
- Piercing the Diaphragm: At the cable entry hole, pierce the rubber diaphragm to allow for the cable to pass through while maintaining a dust and moisture-resistant seal.
- Clamping the Cable Ends: Secure the cable ends using plastic fiber guide posts within the termination box to ensure stability and proper alignment.
- Splicing: Utilize a splicing machine to connect the optical fibers from the cable to the pigtails that lead to the network equipment.
- Testing and Maintenance: After successful splicing, test the connections for signal integrity and make any necessary adjustments. Regular maintenance checks are crucial to ensure long-term performance.
Detailed steps for each of these processes can be found on FiberCheap’s guide to fiber termination box installation.
Tools Required for Installation
A proper set of tools is essential for a smooth installation process. Here is a list of tools you’ll need:
- Fiber optic splicing machine
- Cable stripping tools
- Scissors or precision cutting tools
- Fiber optic cleaning supplies (reagent alcohol and wipes)
- Fusion splicer and cleaver
- Fiber optic testers such as OTDR (Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer)
- Screwdriver set for mounting hardware
- Labeling machine for cable management
These tools are necessary to handle optical fibers delicately and to ensure the connections within the termination box are secure and effective. The quality of the installation will significantly affect the fiber network’s functionality, so it’s also essential to consider the fiber termination box price and invest in high-quality equipment and tools.
The installation process involves precision and attention to detail at every step. Following these guidelines will help you achieve a stable and high-performing fiber optic network infrastructure.
Fiber Termination Box Applications
Fiber termination boxes (FTBs) are pivotal in managing and protecting fiber optic connections within a network. As the bridge between external fiber cables and internal wiring, they serve an indispensable role in fiber optic infrastructures. Let’s delve into the various applications of FTBs in both indoor and outdoor settings.
Indoor Applications
Indoor fiber distribution terminals are designed to be compact and efficient, catering to the installation needs within small to mid-sized Multi-Dwelling Units (MDUs) or Multiple Tenant Units (MTUs). This is especially critical in urban environments where space is at a premium and the organization of fiber cables is essential for maintenance and future scalability.
In residential settings, FTBs are often installed in basements, utility closets, or dedicated telecommunications rooms. They facilitate the distribution of fiber connections to individual units, ensuring that each resident has access to high-speed internet services. In commercial buildings, similar setups are employed, with FTBs placed in server rooms or communication closets to manage the distribution of fiber optic links to various offices or retail spaces.
Here, the fiber termination box wall mount feature proves to be invaluable, allowing for a secure and space-saving installation. These wall-mounted boxes not only organize and safeguard the delicate fiber connections but also ensure easy access for technicians during installation, maintenance, or upgrades.
Outdoor Applications
For outdoor environments, FTBs are designed to withstand the elements, providing a robust solution for the distribution and protection of fiber optic links. They are commonly used in small to medium-sized MDUs as part of the Fiber to the Home (FTTH) networks. These outdoor Fiber Distribution Terminals are essential for bringing high-speed internet access to various residential and business units.
The outdoor FTBs are built to resist environmental factors such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, and UV radiation, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the fiber optic network. They are typically mounted on exterior walls, utility poles, or in underground vaults to maximize protection and facilitate easy access for network expansion or troubleshooting.
Given their crucial role in the expansive reach of fiber networks, it’s important to consider the fiber termination box price as part of the overall investment in a fiber optic infrastructure. The cost-effectiveness of FTBs, combined with their flexibility and protective features, make them an essential component in both indoor and outdoor fiber network installations.
Whether for indoor or outdoor use, fiber termination boxes play a fundamental role in creating a stable and scalable fiber optic network. Their applications in safely distributing and managing optical fiber links are integral to the successful deployment of fiber communication networks. As we continue to rely on high-speed internet connections, the importance of proper FTB installation and maintenance remains paramount.
Quality Considerations for Fiber Termination
In the process of fiber termination box installation, maintaining the integrity of the signal is of paramount importance. There are several factors that contribute to the quality of fiber termination, which, in turn, affect the overall performance of the fiber optic network. We’ll explore two critical aspects: achieving minimal signal loss and ensuring resistance to environmental factors.
Achieving Minimal Signal Loss
To achieve minimal signal loss, a high-quality fiber termination system is essential. Such a system ensures minimal back reflection, which is crucial for maintaining the strength and clarity of the transmitted signal. According to STL.tech, proper fiber laying and termination should result in low signal loss, which is a key indicator of a well-installed network.
Key factors to minimal signal loss include:
- Quality of fiber optic cables
- Precision in cutting and splicing the fiber
- Use of high-quality connectors and termination boxes
It’s also imperative to conduct regular inspections of the cables and the termination points to detect any potential issues that might contribute to signal degradation. Ensuring that the termination box and connections are clean and free from contaminants is a part of routine maintenance that helps preserve signal integrity.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Fiber termination must not only ensure signal integrity but also withstand a variety of environmental factors such as moisture, impact, chemical exposure, and thermal cycling. A well-designed fiber termination system will feature resistance to these elements, thereby protecting the network’s performance over time.
Here are some of the measures to ensure environmental resistance:
- Using termination boxes with high-quality seals and gaskets to prevent moisture infiltration, which can lead to corrosion and impact network performance. Some fiber splicer closures meet waterproof IP68 standards, as noted by BAUDCOM.
- Implementing impact-resistant designs to safeguard against physical damage that can occur during handling or installation.
- Ensuring that the termination box is made from materials that can withstand chemical exposure, which is particularly important in industrial environments.
- Choosing termination boxes that are designed to handle the thermal cycling associated with outdoor installations, where temperatures can fluctuate widely.
By addressing these quality considerations, we can ensure that our fiber termination not only facilitates clear and consistent signal transmission but also stands the test of time against environmental challenges. Remember to explore options for both fiber termination box wall mount and fiber termination box price to find the best fit for your specific needs.
Troubleshooting Fiber Termination Issues
When we install fiber termination boxes, we sometimes encounter challenges that can impact the performance and reliability of the network. In this section, we will address common issues with fiber splice closures and how to correct fiber misalignment, which are critical to maintaining a high-functioning fiber optic network.
Common Issues with Fiber Splice Closures
Fiber splice closures are vital in protecting fiber optic connections, but they can also be a source of issues if not handled properly. One of the most frequent problems is damage to the fiber optic cable, which can arise from excessive bending, crushing, or twisting. This damage can lead to signal loss, poor performance, or complete network failure. To address this, we must carefully inspect the cables and splice closures for signs of damage and repair or replace them as needed to prevent further problems (BAUDCOM).
Another issue is moisture infiltration, which can cause water damage to cables and components, leading to corrosion and degraded network performance. To combat this, we need to ensure that splice closures are effectively sealed and protected from moisture with high-quality seals and gaskets, along with regular inspections for signs of infiltration. Certain products, like those from Baudcom, meet waterproof IP68 standards, which offer robust protection against moisture (BAUDCOM).
Cable strain is another challenge that can arise due to excessively tight cable pulling or incorrect installation of the splice closure. To mitigate this, cables must be properly secured and supported to prevent unnecessary strain or tension, ensuring the stability of the network connections (BAUDCOM).
For more detailed information about fiber termination boxes and their installation, including wall-mounted options, check out our guide on fiber termination box wall mount and review the fiber termination box price for budget considerations.
How to Address Fiber Misalignment
Fiber misalignment is a prevalent issue that can result from improper installation or changes in temperature, leading to attenuation or signal loss. To correct this issue, we need to open the fiber optic splice closure and carefully inspect the fibers for any misalignment. If found, repositioning and splicing the fibers together again is necessary (BAUDCOM).
Poor connection quality is often due to dirty connectors, damaged connectors, or the use of subpar splicing tools. To address this issue, we conduct a thorough inspection of the splice closure and fiber optic cables for defects. This may require re-splicing using high-quality tools and connectors or replacing damaged components to enhance connection quality.
By understanding how to troubleshoot these common issues, we can ensure the success of our fiber termination box installation and maintain the integrity of our network. It is crucial to follow best practices and use the appropriate tools and techniques to prevent these problems from occurring in the first place.
Best Practices for Fiber Termination
To ensure the success and reliability of a fiber termination box installation, it’s critical to adhere to a set of best practices, from proper fiber handling to conducting meticulous quality testing.
Proper Fiber Handling Techniques
When we handle fiber cables, we must be meticulous to protect the delicate strands within. Proper fiber handling includes precision cleaving, thorough fiber cleaning, and careful alignment and fusion techniques. These are crucial best practices for achieving reliable and successful fiber cable splicing within fiber splice enclosures (FS Community).
Here are a few key handling techniques:
- Cleaving: Use high-quality cleavers to ensure a smooth, flat end-face that is perpendicular to the fiber axis.
- Cleaning: Remove contaminants such as dust and oil from fiber ends with specialized cleaning tools or fluids. This prevents impurities from affecting signal quality.
- Stripping: Employ fiber optic three-hole jacket strippers to remove the outer jacket and inner strand coatings without damaging the fiber (TechLogix Network).
- Measuring and Marking: Accurately measure and mark the fiber using a metric ruler and marker to ensure precise cuts and alignments.
By following these techniques and using the correct tools, we can significantly reduce the risk of signal loss and ensure a robust connection.
Quality Testing Procedures
After the fibers are terminated and housed within the fiber termination box, it is imperative to carry out quality testing to verify the integrity of the connections. This process involves using power meters, Optical Time Domain Reflectometers (OTDRs), or other equipment to ensure accurate data transmission and signal integrity (FS Community).
The following is an outline of a basic quality testing procedure:
- Visual Inspection: Use a fiber optic microscope to check for any evident flaws or imperfections on the fiber end-face.
- Signal Loss Testing: Utilize a power meter to measure the amount of light being transmitted through the fiber to detect any significant loss.
- Reflectance Testing: With an OTDR, measure the backscattered light in the fiber to identify any issues with splice quality or connection points.
| Test Type | Tool Required | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Fiber Optic Microscope | Check for imperfections |
| Signal Loss | Power Meter | Measure light transmission |
| Reflectance | OTDR | Identify splice/connection issues |
Regular testing and maintenance can prevent future problems and ensure that the fiber termination box performs as expected. It is also a good practice to maintain detailed records of all tests for future reference and troubleshooting.
By integrating these best practices for fiber handling and quality testing into our fiber termination box installation process, we can guarantee a higher level of precision and reliability in our fiber optic networks.
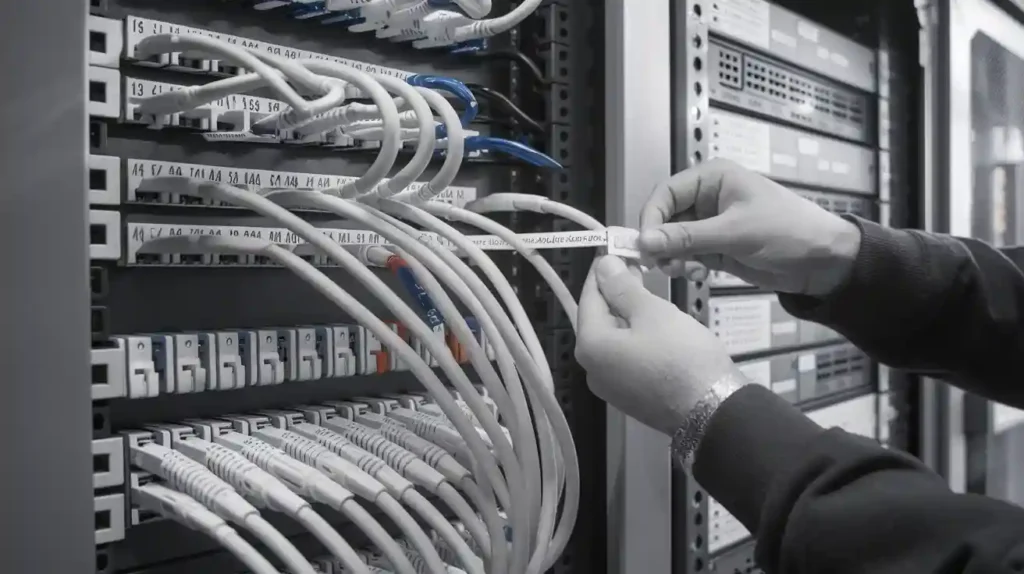











 Fiber Optic Termination Boxes
Fiber Optic Termination Boxes Fiber Optic Splice Enclosures
Fiber Optic Splice Enclosures Fiber Patch Panels
Fiber Patch Panels PLC Splitters
PLC Splitters Fiber Optic Pigtails
Fiber Optic Pigtails OTDR Launch Cables
OTDR Launch Cables Fiber Optic Adapters
Fiber Optic Adapters Fiber Optic Patch Cords
Fiber Optic Patch Cords